Vietnam's microbiological technology: Current status and development trends
The results of developing a technology map in microbiology technology for socio-economic development have basically assessed and clearly analyzed important issues of the current industry, such as the current state of microbiological technology in microbiological industries. Vietnam's manufacturing industry, the potential demand of the market, the level of technology requirements, the ability to develop technology, the development trend of microbiology technology in the world. On the basis of the achieved results, a number of development orientations of microbiological technology in the coming time have been identified and proposed based on 3 main groups (technology, infrastructure and applications) and 3 levels (national level). country, industry/sector and enterprise). These orientations make an important contribution to the formulation of biotechnological development strategies in the coming time, as well as serve as a basis for building orders for research, application and technological innovation tasks of the company. research institutes, universities and businesses.

Current status of microbiological technology in Vietnam
Microbiological technology includes 4 main groups of technologies, including: breeding technology, seed preservation technology, fermentation technology, recovery technology and product creation. The results of building technology maps have basically determined the current status of 4 groups of technologies as follows:
About the breed
This is the first factor in the production process, which determines the productivity, quality and characteristics of the end product. Vietnam has a relatively complete range of seed strains, but the strains are still in rudimentary form, the expression efficiency is not high, and the stability of the strains is still limited. The number of seed strains put into industrial production is not much, most of them have to be imported.
For example, strains for the production of beer, wine, beverages, yogurt, biologically active ingredients (antibiotics, enzymes, vitamins, etc.) must be imported from abroad. Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, currently Vietnam has a collection of about 800 strains (Institute of Food Industry - Ministry of Industry and Trade) and is used to produce a few beer products. However, some major brewers (SABECO, HABECO) still have to import foreign strains because: 1) imported varieties are genetically stable (controlled and stable in terms of yield, quality, and taste). ); 2) specific strains; 3) psychopathic devotion.
In vaccine production, there are currently no databases and banks on strains of pathogens in Vietnam. Monitoring and collection of sample sources is only done separately at each research facility/enterprise, with little cooperation in information sharing. Research on the immune properties and protective ability of vaccine-producing strains against field strains in Vietnam still has some limitations (usually only evaluating the protection of the same strain, there are few possible evaluations of the same species). cross protection between strains). In vitro studies are often based mainly on cellular immunological properties, without regard to other characteristics.
Seed preservation technology
This is an intermediate stage in the production process, affecting the stability and survivability of the seed strain. Preservation of seed strains in Vietnam uses freeze-drying and deep freezing methods that approach world technology (eg, strains used in vaccine production). However, pretreatment techniques and preservatives are still limited.
Conventional preservation technologies such as preservation on agar, in glycerol, on sand, on seeds reach the world level. However, these technologies are old and rarely used in the world.
Fermentation technology
It is the stage that determines the output and production scale; affect the cost of products in the same production technology. In some applications, Vietnamese enterprises have synchronous investment equivalent to the world such as: animal feed, beer, wine, yogurt, vaccines for humans and animals. In a number of other applications, relative mastery of fermentation technology processes has been achieved at laboratory and pilot scale.
The synchronization and integration of technology and equipment is not high, the automation ability is low, mainly batch or semi-continuous fermentation, so productivity and output are still low. There are no studies on optimizing conditions for large-volume fermentation or maximizing active ingredients of interest, but only focusing on biomass production. For example, the strain Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is used in the production of biopesticides. Vietnam currently has a seed collection with 3,700 strains, which are kept mainly at the Institute of Biotechnology, of which 400 strains have been described in detail and evaluated genetic resources, have produced 5 pilot scale. m3 and has been applied in crop protection (vegetables, fruit trees and rice) since 1983 in Hanoi, Lam Dong and Ho Chi Minh City. However, at present, Bt preparations still have to be imported.
Technology for recovery and product creation
Technology of product recovery and creation plays a decisive role in product standards, quality and specifications. The higher the requirements for products and applications in terms of purity, content and quality control, the more important the role of recovery and product generation technology (e.g. vaccine production, operations, etc.) biological substances, drugs, etc.). Vietnam has basically mastered the technology of recovery and product creation for applications that directly use microbial biomass in agriculture and the environment, a part of which uses pure active ingredients such as in industry. industry and healthcare.
However, it can be seen that the current recalling technologies in Vietnam are only basic, without advanced technologies, leading to low product quality and short product preservation time. The technology to create products (formulation) for some products preserved for a long time but still retain their activity, properties and viability (biomass preparations) in the country is still poor compared to the world. For example, Vietnam's digestive enzyme products (probiotics) are mainly in powder form (freeze-dried), while in the world are packaged in microcapsules.
Thus, the overall assessment shows that the level of microbiological technology in Vietnam is above average and not too different from the world, but it is still weak in important technologies. Due to the lack of concentrated resources, synchronous investment, partly due to high investment costs while the market capacity is not large enough and the specialization in the business community is still low. Many advanced, high-performance, large-scale microbiological technologies are not yet ready in our country
Vietnam also does not have trial production centers large and modern enough to serve the development of microbiological technology. The existing infrastructure system such as research and production equipment to create biotechnology products by microbiological technology is still limited and inconsistent, making research products in laboratories and experimental workshops difficult to bring to market. Information technology infrastructure and analysis software have not been properly invested to achieve the highest efficiency. In addition, Vietnam currently lacks human resources with high qualifications in research, development and application to production as well as human resources with specialized training in bioinformatics technology.
Trends in research and development of microbiology technology in the world
Microbiological technology is currently developing strongly in the world focusing on biosynthesis. The combination of modern microbiology, nanotechnology, information technology and artificial intelligence can open up new technology models and become the future trend.
The major issues of microbiology being studied in the world include:
1. Research on the earth's microbiome (Earth Microbiome).
2. Researching the human microbiome (Human Microbiome), including the major content: the human gut microbiome (considered the second DNA system, as well as the second human brain). Study of human gut microbiome reveals the relationship between microorganisms and human disease to develop therapeutic methods, products and preparations such as: gut microbiome study reveals microbial associations new bacteria with diabetes; bacterial DNA marker in blood points to new universal cancer test; toxins produced by gut bacteria are commonly associated with bowel cancer; gut microbiota suggest new treatment for enteritis; studying the effects of diet and the microbiome on the heart and aging; research and development of AI for age prediction based on gut, skin and oral microbiota; research exploring the link between personality and gut microbiota; gut bacteria reduce the severity of Parkinson's disease; airway microbiome associated with childhood asthma; increased risk of bowel cancer associated with intestinal bacterial species; study that sunlight on the skin directly affects the gut microbiota; Microbiome affects serotonin in the gut and blood sugar...
Proposing the development orientation of microbiology technology in Vietnam
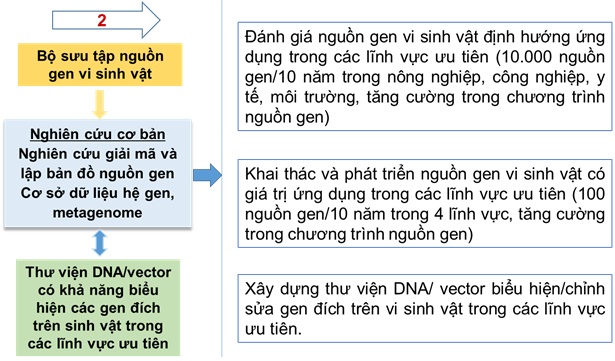
To determine the development direction of microbiological technology in Vietnam, a number of analytical methods are used, including: assessment of the current status, technological capacity in research and production; assess the role and popularity of technology; identify technology trends; analysis of social needs. In which, priority products/applications are evaluated and selected according to the following criteria: determining the development potential of application groups based on evaluation criteria of markets in the world and in Vietnam. current (size, market share), general development trends and priority policies of Vietnam; assess the level of technology requirements and determine the correlation between the needs of the market and the level of technology requirements to select appropriate priority product/application groups.
On that basis, 9 priority product groups were identified, including: veterinary drugs and vaccines; human vaccines; biopharmaceuticals; preparations for the treatment of solid waste and wastewater; feed additives, aquaculture and animal probiotics; biologically active substances in therapeutic support; microbial organic fertilizers and agricultural products; biological plant protection drugs; acids and organic solvents. Based on selected priority products, priority technologies are further determined based on aggregated evaluation criteria such as technology trends, expert assessment, technology mastery, dissemination of technology and technology related to priority products.
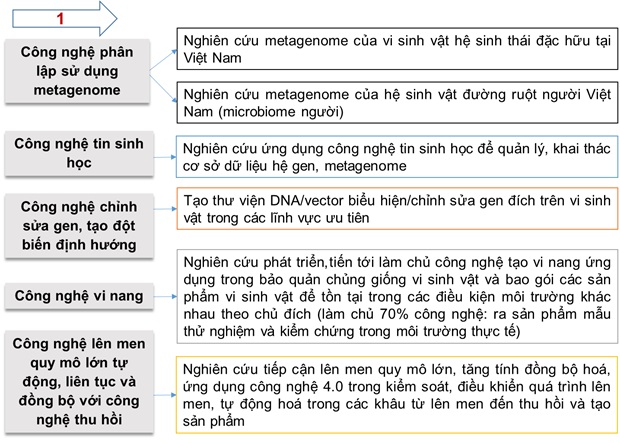
The prioritized technologies are identified as directional mutagenesis technologies, improving expression performance; isolation technology using metagenomics, combining techniques of molecular biology and bioinformatics in microbial breeding. Pretreatment technology: critical stress, use of antifreeze, antioxidants in seed preservation. Research on large-scale fermentation approach, increase synchronization, application of 4.0 technology in controlling and controlling the fermentation process, automation in stages. In product recovery and creation, the research approaches synchronously and continuously with fermentation systems, applying 4.0 technology in control, control and automation in stages.
As a result, the research team selected 9 priority application groups (including 29 specific products/applications) and 15 technologies that need to be prioritized for development for the period up to 2040 (tables 1, 2). .
Table 1. List of products/applications that need to be prioritized for development in microbiology in Vietnam.
|
Thứ tự |
Sản phẩm/ứng dụng |
Chi tiết |
|
1 |
Thuốc và vắc-xin thú y |
Vắc-xin đa giá Vắc-xin tái tổ hợp Vắc-xin khác Kháng sinh động vật KIT chẩn đoán bệnh động vật |
|
2 |
Vắc-xin cho người |
Vắc-xin tái tổ hợp Vắc-xin cộng hợp Vắc-xin kết hợp Vắc-xin vỏ virus Vắc-xin khác |
|
3 |
Dược phẩm sinh học |
Kháng sinh thế hệ mới Kháng sinh nhóm cephalosporins Kháng sinh chống ung thư Vitamin và axit amin (tự nhiên và tái tổ hợp) |
|
4 |
Chế phẩm xử lý chất thải rắn và nước thải |
Xử lý chất thải rắn và nước thải sinh hoạt Xử lý chất thải rắn và nước thải trong chăn nuôi và giết mổ gia súc, gia cầm; chế biến thủy sản, công nghiệp, nông nghiệp Xử lý chất thải y tế |
|
5 |
Phụ gia thức ăn chăn nuôi, nuôi trồng thuỷ sản và probiotic động vật |
Protein, axit amin, prebiotic, synbiotic Probiotic trong chăn nuôi, nuôi trồng thuỷ sản |
|
6 |
Chất hoạt tính sinh học trong hỗ trợ điều trị |
Interferon, cytokine, interleukin, hormone Kháng thể liệu pháp Thực phẩm chức năng nguồn gốc vi sinh |
|
7 |
Phân hữu cơ vi sinh và chế phẩm nông nghiệp |
Phân hữu cơ vi sinh đa chức năng |
|
8 |
Thuốc bảo vệ thực vật sinh học |
Thuốc TSSH Bacillus thuringiensis Thuốc SH đa chức năng |
|
9 |
Axit và dung môi hữu cơ |
Axit axetic, axit citric, axit lactic Acetone, Butanol, Methanol, Ethanol Hương liệu thực phẩm và mỹ phẩm |
Table 2. List of technologies to be prioritized.
|
|
Công nghệ |
Mục tiêu đề ra |
|
Tạo giống |
Công nghệ DNA tái tổ hợp Công nghệ chỉnh sửa gen Công nghệ phân lập |
Công nghệ tạo đột biến định hướng, nâng cao hiệu suất biểu hiện Công nghệ phân lập sử dụng metagenomics, kết hợp các kỹ thuật sinh học phân tử và tin sinh học |
|
Công nghệ bảo quản giống |
Công nghệ lạnh sâu Công nghệ đông khô |
Công nghệ tiền xử lý: ứng suất tới hạn, sử dụng các chất chống đông, chất chống oxy hoá |
|
Công nghệ lên men |
Công nghệ lên men chìm theo mẻ (nâng cao năng suất, hiệu suất) Công nghệ lên men chìm theo mẻ bổ sung Công nghệ lên men liên tục Công nghệ lên men bề mặt trạng thái rắn |
Nghiên cứu tiếp cận lên men quy mô lớn, tăng tính đồng bộ hoá, ứng dụng công nghệ 4.0 trong kiểm soát, điều khiển quá trình lên men, tự động hoá trong các khâu |
|
Công nghệ thu hồi và tạo sản phẩm |
Công nghệ lọc tiếp tuyến Công nghệ ly tâm liên tục, siêu ly tâm Công nghệ sấy phun Công nghệ tạo vi nang Công nghệ thu hồi sản phẩm phi sinh khối sắc ký Công nghệ thu hồi sản phẩm phi sinh khối thẩm tích |
Nghiên cứu tiếp cận hướng đồng bộ và liên tục cùng các hệ thống lên men, ứng dụng công nghệ 4.0 trong kiểm soát, điều khiển, tự động hoá trong các khâu |
To ensure resources for the development of priority application/product and technology groups, in addition to appropriate investment in a system of laboratories, test production centers and high-quality human resources, The development of the collection of microbial genetic resources is also an important content that should be prioritized in the coming time. Developing a collection of microbial genetic resources along with priority technologies and product groups form three closely related pillars (figure 1).
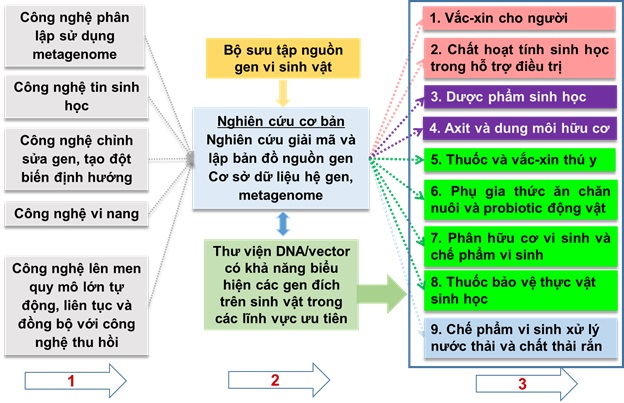
Figure 1. Relationship between technologies and product groups to prioritize development.
Based on these three pillars, research and development issues to be solved are set out and clarified for each pillar. The first pillar is a list of a number of key technologies that need to be prioritized for development in the near future and corresponding to each given technology, the main research and development content to be solved is identified as shown in the figure below. 2
The second pillar group shows that the collection of microbial genetic resources plays an important role in the collection, research and development of genetic resources in a selective, oriented way to serve as a basic foundation for the selection and breeding of microorganisms. produce quality microorganisms, meeting the requirements of increasingly high production. This is also the main trend in the world today as analyzed above and clarified in Figure 3 .
Conclusion
According to the "Master plan for development and application of biotechnology in Vietnam to 2020" approved by the Prime Minister on January 22, 2008, the development and application of biotechnology will focus on mainly in the fields of agriculture - forestry - fishery, food processing industry, food hygiene and safety, medicine - pharmacy and human health protection, environmental protection.
The overall view is to build and develop the bio-industry in our country to become a spearhead economic-technical industry, playing an important role, effectively serving the cause of industrialization and modernization of the country. and widely and effectively apply biotechnology to production and life.
In the context of limited national resources, the orientation of science and technology (S&T) activities focusing on specific goals is very important for the effective development of science and technology and contributing to the development of science and technology. contributing to the development of economic sectors in certain periods. The results given above are an important basis for formulating plans for implementing technological innovation activities, improving the competitiveness of enterprises, contributing to the implementation of national programs, contributing to the orientation of enterprises. for S&T development programs in the coming period as well as enhancing the role of S&T in socio-economic development in general and microbiology in particular.
REFERENCES
1. Directive No. 50-CT/TW on promoting development and application of biotechnology to serve the cause of industrialization and modernization of the country, promulgated on March 4, 2005.
2. Le Nhu Kieu, Ngo Dinh Binh, Nguyen Duc Hoang, Le Trong Tai (2020), “Evaluating the current situation of production and application of microbial products and proposing orientations for development of microbial technology in agriculture in Vietnam", Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology of Vietnam, 3(112), pp.98-106.
3. Resolution No. 18/CP on biotechnology development in Vietnam until 2010, issued on 11/3/1994.
4. Quan Le Ha, Ngo Dinh Binh, Nguyen Duc Hoang, Le Trong Tai, Ta Viet Dung (2020), "Development of microbiological technology in industry in Vietnam", Vietnam Science and Technology Journal, 5, p. 30-33.
5. Decision No. 11/2006/QD-TTg approving "Key program for development and application of biotechnology in the field of agriculture and rural development until 2020", issued on 12/02 January 2006.
6. Decision No. 97/2007/QD-TTg approving the "Project on development and application of biotechnology in the fisheries sector until 2020", issued on June 29, 2007.
7. Decision No. 14/2007/QD-TTg on approving “Project on development and application of biotechnology in the field of processing industry until 2020”, issued on January 25, 2007.
8. Decision No. 2457/QD-TTg approving the National High-tech Development Program to 2020, issued on December 31, 2010.
9. Decision No. 3056/QD-BKHCN on amending the name, approving the objectives, contents and expected products of the key State-level Science and Technology Program for the period 2011-2015: “Research, development and application use of biotechnology", issued on September 30, 2011.
10. Decision No. 850/QD-TTg approving “Project on construction of key laboratories”, issued on September 7, 2000.
11. Decision No. 3771/QD-BKHCN on promulgating the "Guideline for building technology maps, technology roadmap and technological innovation", issued on December 13, 2019.